The Indian Economic Service (IES) Syllabus is an essential guide for candidates preparing for the UPSC IES / ISS Exam. Indian Economic Service (IES) Syllabus covers essential topics such as Microeconomics, Macroeconomics, Public Finance, Statistics, Econometrics and Indian Economics, the syllabus is designed to test both theoretical knowledge and practical application of economic concepts. To succeed in Indian Economic Service (IES), candidates must focus on understanding each subject in-depth, as the exam challenges them to analyze and solve real-world economic problems. A detailed and strategic approach to the Indian Economic Service (IES) Syllabus is key to clearing this highly competitive examination and achieving success in the field of economics.
Indian Economic Service Exam Pattern
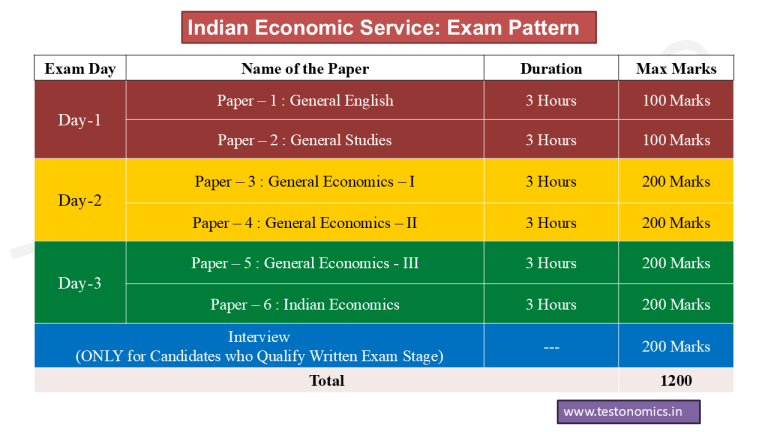
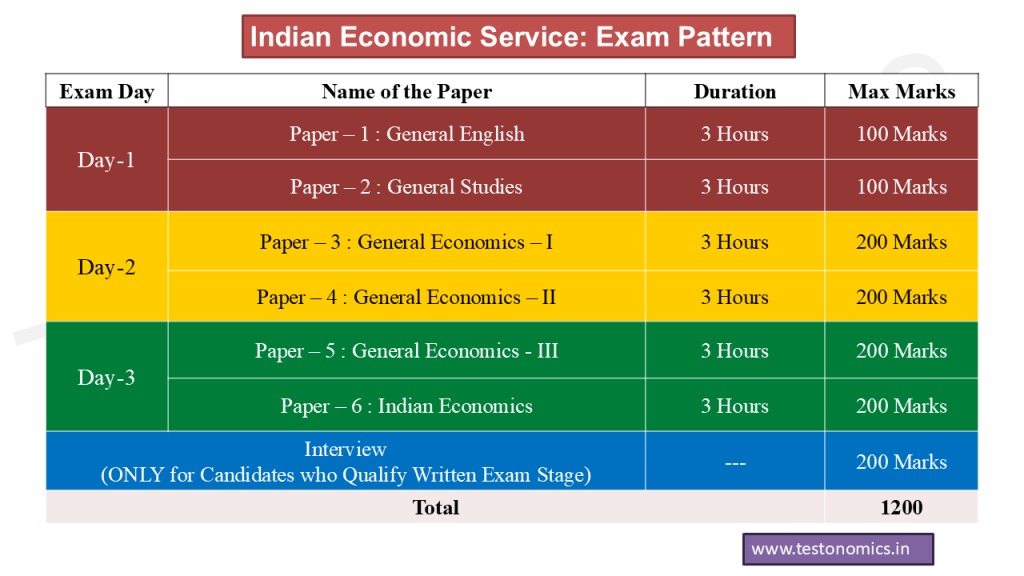
Let us now discuss the Indian Economic Service Exam Pattern. The Indian Economic Service (IES) Exam Pattern consists of 6 Papers conducted over 3 consecutive days, with 2 papers being conducted on each day. The 6 Papers are (1)General English : 100 Marks (2)General Studies :100 Marks (3)General Economics-I : 200 Marks (4)General Economics-II : 200 Marks (5) General Economics-III : 200 Marks (6)Indian Economics : 200 Marks.
Indian Economic Service (IES) Syllabus
We now shift our attention to a detailed discussion of Indian Economic Service (IES) Syllabus and understand how to complete it thoroughly. The Indian Economic Service (IES) Syllabus consists of all subjects from core Economics, including Microeconomics, Macroeconomics, Statistics, Econometrics Public Finance, Growth & Development, International Economics, etc.
Day 1 : General english and General Studies
The Indian Economic Service (IES) Syllabus begins with the English paper. On Day-1 of the Indian Economic Service (IES) Exam, candidates have to write 2 papers : General English in the morning session and General Studies in the afternoon session. The total marks devoted to both these papers are 200 !
Paper-1: General English Syllabus
In the English paper of Indian Economic Service (IES) Exam, candidates will be required to write an essay in English. Other questions will be designed to test their understanding of English and workman like use of words. Passages will usually be set for summary or precis.
Paper-2: General Studies Syllabus
In the General Studies Paper of the Indian Economic Service (IES) Exam, candidates will be tested on General knowledge including knowledge of current events and of such matters of everyday observation and experience in their scientific aspects as may be expected of an educated person who has not made a special study of any scientific subject. The paper will also include questions on Indian Polity including the political system and the Constitution of India, History of India and Geography of a nature which a candidate should be able to answer without special study
Day-2
On Day-2 of the Indian Economic Service (IES) Exam, candidates have to write the third and fourth papers, (3)General Economics-I and (4)General Economics-II. Both these papers are a very important part of In IES Syllabus and a serious candidate should target a combined score of 210+ in both these papers, out of the maximum 400 marks devoted to both these papers
Paper-3: GENERAL ECONOMICS - I
Theory of Consumer’s Demand
Cardinal Utility Analysis: Marginal utility and demand, Consumer’s surplus, Indifference curve Analysis and utility function, Price, income and substitution effects, Slutsky theorem and derivation of demand curve, Revealed preference theory. Duality and indirect utility function and expenditure function, Choice under risk and uncertainty. Simple games of complete information, Concept of Nash equilibrium.
Theory of Production
Theory of Production: Factors of production and production function. Forms of Production Functions: Cobb Douglas, CES and Fixed coefficient type, Translog production function. Laws of return, Returns to scale and Return to factors of production. Duality and cost function, Measures of productive efficiency of firms, technical and allocative efficiency. Partial Equilibrium versus General Equilibrium approach. Equilibrium of the firm and industry
Theory of Value
Pricing under different market structures, public sector pricing, marginal cost pricing, peak load pricing, cross-subsidy free pricing and average cost pricing. Marshallian and Walrasian stability analysis. Pricing with incomplete information and moral hazard problems.
Theory of Distribution
Neo classical distribution theories; Marginal productivity theory of determination of factor prices, Factor shares and adding up problems. Euler’s theorem, Pricing of factors under imperfect competition, monopoly and bilateral monopoly. Macrodistribution theories of Ricardo, Marx, Kaldor, Kalecki.
Welfare Economics
Inter-personal comparison and aggression problem, Public goods and externalities, Divergence between social and private welfare, compensation principle. Pareto optimality. Social choice and other recent schools, including Coase and Sen
Mathematical Methods in Economics
Differentiation and Integration and their application in economics. Optimisation techniques, Sets, Matrices and their application in economics. Linear algebra and Linear programming in economics and Input-output model of Leontief
Statistical and Econometric Methods
Differentiation and Integration and their application in economics. Optimisation techniques, Sets, Matrices and their application in economics. Linear algebra and Linear programming in economics and Input-output model of Leontief
Paper-4: General Economics II
The General Economics II syllabus of IES Syllabus contains topics from Macroeconomics, Growth & Development, International Economics, etc.
Economic Thought
Mercantilism Physiocrats, Classical, Marxist, Neo-classical, Keynesian and Monetarist schools of thought
Concept of National Income and Social Accounting
Measurement of National Income, Inter relationship between three measures of national income in the presence of Government sector and International transactions. Environmental considerations, Green national income
Theory of employment, Output, Inflation, Money and Finance
The Classical theory of Employment and Output and Neo classical approaches. Equilibrium, analysis under classical and neo classical approach. Keynesian theory of Employment and Output. Post Keynesian developments. The inflationary gap; Demand pull versus cost push inflation, the Philip’s curve and its policy implication. Classical theory of Money, Quantity theory of Money. Friedman’s restatement of the quantity theory, the neutrality of money. The supply and demand for loanable funds and equilibrium in financial markets, Keynes’ theory on demand for money. IS-LM Model and AD-AS Model in Keynesian Theory.
Financial and Capital Market
Finance and economic development, financial markets, stock market, gilt market, banking and insurance. Equity markets, Role of primary and secondary markets and efficiency, Derivatives markets; Future and options
Economic Growth and Development
Concepts of Economic Growth and Development and their measurement: characteristics of less developed countries and obstacles to their development – growth, poverty and income distribution. Theories of growth: Classical Approach: Adam Smith, Marx and Schumpeter- Neo classical approach; Robinson, Solow, Kaldor and Harrod Domar. Theories of Economic Development, Rostow, Rosenstein-Roden, Nurske, Hirschman, Leibenstien and Arthur Lewis, Amin and Frank (Dependency school) respective role of state and the market. Utilitarian and Welfarist approach to social development and A.K. Sen’s critique. Sen’s capability approach to economic development. The Human Development Index. Physical quality of Life Index and Human Poverty Index. Basics of Endogenous Growth Theory
International Economics
Gains from International Trade, Terms of Trade, policy, international trade and economic development- Theories of International Trade; Ricardo, Haberler, Heckscher- Ohlin and Stopler- Samuelson- Theory of Tariffs- Regional Trade Arrangements. Asian Financial Crisis of 1997, Global Financial Crisis of 2008 and Euro Zone Crisis- Causes and Impact.
Balance of Payments
Disequilibrium in Balance of Payments, Mechanism of Adjustments, Foreign Trade Multiplier, Exchange Rates, Import and Exchange Controls and Multiple Exchange Rates. IS-LM Model and Mundell- Fleming Model of Balance of Payments
Global Institutions
UN agencies dealing with economic aspects, role of Multilateral Development Bodies (MDBs), such as World Bank, IMF and WTO, Multinational Corporations. G-20
DAY-3
On Day-3 of the Indian Economic Service Exam, the candidate has to appear for the fifth and sixth papers, viz., General Economics-III and Indian Economics. Remember, that you would have already written 4 papers on 2 previous days of Indian Economic Service (IES) Exam and thus you would already begin to feel tired. The third day of Indian Economic Service is very important again. To do your best, make sure you have already completed many rounds of revisions of the IES Syllabus : General Economics-III and Indian Economics papers.
Paper-5: General Economics III
The General Economics III paper of Indian Economic Service Syllabus contains topics from Public Finance, Environmental Economics and Planning.
Public Finance
Theories of taxation: Optimal taxes and tax reforms, incidence of taxation. Theories of public expenditure: objectives and effects of public expenditure, public expenditure policy and social cost benefit analysis, criteria of public investment decisions, social rate of discount, shadow prices of investment, unskilled labour and foreign exchange. Budgetary deficits. Theory of public debt management.
Environmental Economics
Environmentally sustainable development, Rio process 1992 to 2012, Green GDP, UN Methodology of Integrated Environmental and Economic Accounting. Environmental Values: Users and Non-Users values, option value. Valuation Methods: Stated and revealed preference methods. Design of Environmental Policy Instruments: Pollution taxes and Pollution permits, collective action and informal regulation by local communities. Theories of exhaustible and renewable resources. International environmental agreements, RIO Conventions. Climatic change problems. Kyoto protocol, UNFCC, Bali Action Plan, Agreements up to 2017, tradable permits and carbon taxes. Carbon Markets and Market Mechanisms. Climate Change Finance and Green Climate Fund
Industrial Economics
Market structure, conduct and performance of firms, product differentiation and market concentration, monopolistic price theory and oligopolistic interdependence and pricing, entry preventing pricing, micro level investment decisions and the behaviour of firms, research and development and innovation, market structure and profitability, public policy and development of firms
State, Market and Planning
Planning in a developing economy. Planning regulation and market. Indicative planning. Decentralised planning
Paper-6: Indian Economics
The Indian Economics paper of Indian Economic Service (IES) Exam Syllabus tests candidates' in-depth understanding of post-independence developments in Indian Economy, including the Static portion and Indian Economy Current Affairs.
History of Development and Planning
Alternative development strategies—goal of self-reliance based on import substitution and protection, the post-1991 globalisation strategies based on stabilisation and structural adjustment packages: fiscal reforms, financial sector reforms and trade reforms
Federal Finance
Constitutional provisions relating to fiscal and financial powers of the states, Finance Commissions and their formulae for sharing taxes, Financial aspect of Sarkaria Commission Report, Financial aspects of 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments
Budgeting and Fiscal Policy
Tax, expenditure, budgetary deficits, pension and fiscal reforms, Public debt management and reforms, Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, Black money and Parallel economy in India—definition, estimates, genesis, consequences and remedies
Poverty, Unemployment and Human Development
Estimates of inequality and poverty measures for India, appraisal of Government measures, India’s human development record in global perspective. India’s population policy and development
Agriculture and Rural Development Strategies
Technologies and institutions, land relations and land reforms, rural credit, modern farm inputs and marketing— price policy and subsidies; commercialisation and diversification. Rural development programmes including poverty alleviation programmes, development of economic and social infrastructure and New Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme
India’s experience with Urbanisation and Migration
Different types of migratory flows and their impact on the economies of their origin and destination, the process of growth of urban settlements; urban development strategies
Industry: Strategy of industrial development
Strategy of industrial development— Industrial Policy Reform; Reservation Policy relating to small scale industries. Competition policy, Sources of industrial finance. Bank, share market, insurance companies, pension funds, non-banking sources and foreign direct investment, role of foreign capital for direct investment and portfolio investment, Public sector reform, privatisation and disinvestment
Labour
Employment, unemployment and underemployment, industrial relations and labour welfare— strategies for employment generation—Urban labour market and informal sector employment, Report of National Commission on Labour, Social issues relating to labour e.g. Child Labour, Bonded Labour International Labour Standard and its impact
Foreign Trade
Salient features of India’s foreign trade, composition, direction and organisation of trade, recent changes in trade, balance of payments, tariff policy, exchange rate, India and WTO requirements. Bilateral Trade Agreements and their implications
Money and Banking
Financial sector reforms, Organisation of India’s money market, changing roles of the Reserve Bank of India, commercial banks, development finance institutions, foreign banks and non-banking financial institutions, Indian capital market and SEBI, Development in Global Financial Market and its relationship with Indian Financial Sector. Commodity Market in India-Spot and Futures Market, Role of FMC.
Inflation
Definition, trends, estimates, consequences and remedies (control): Wholesale Price Index. Consumer Price Index: components and trends